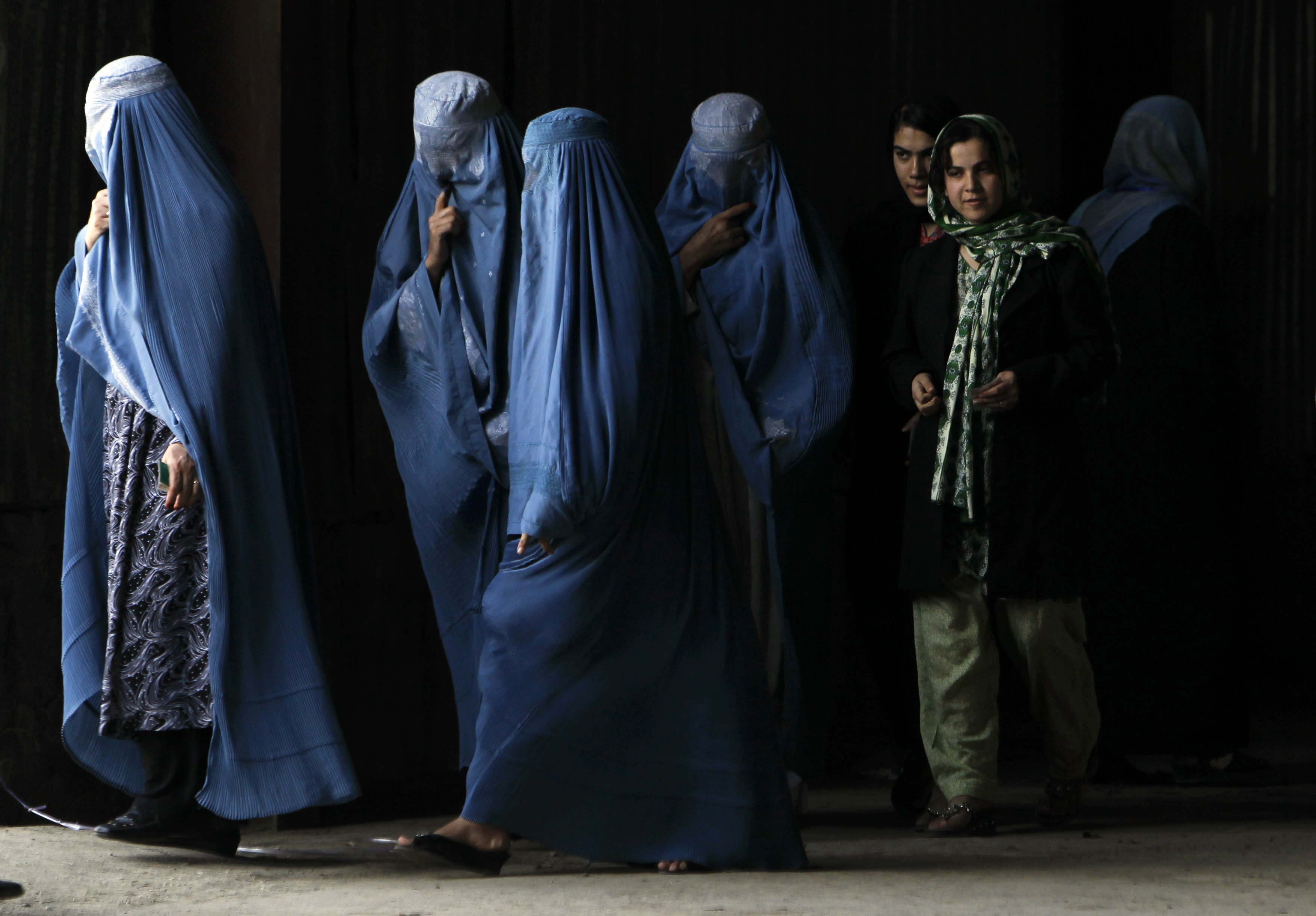
Afghanistan Fails to Protect its Women
Afghanistan Women
NEW DELHI: International human rights watchdog Amnesty International has said that human rights defenders in Afghanistan who face mounting violence - including threats, sexual assault and assassinations- are being abandoned by their own government despite the significant gains they have fought to achieve.
In a report titled “Their Lives On The Line” the organisation documents how champions for the rights of women and girls, including doctors, teachers, lawyers, police and journalists as well as activists have been targeted not just by the Taliban but by warlords and government officials as well. Laws meant to support them are poorly implemented, if at all, while the international community is doing far too little to ease their plight, the report notes.
“Women human rights defenders from all walks of life have fought bravely for some significant gains over the past 14 years – many have even paid with their lives. It’s outrageous that Afghan authorities are leaving them to fend for themselves. , with their situation more dangerous than ever,” said Salil Shetty, Amnesty International’s Secretary General, in Kabul to launch the report.
(2014 saw war-related casualties in Afghanistan reach a record high, with women and children killed also reaching record numbers. Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
“With the troop withdrawal nearly complete, too many in the international community seem happy to sweep Afghanistan under the carpet. We cannot simply abandon this country and those who put their lives on the line for human rights, including women’s rights.”
The report notes that while Taliban are responsible for the majority of attacks against women defenders, government officials or powerful local commanders with the authorities’ backing are increasingly implicated in violence and threats against women.
As one woman defender explained: “The threats now come from all sides: it’s difficult to identify the enemies. They could be family, security agencies, Taliban, politicians.”
“Anti-government groups are targeting prominent and outspoken women’s rights advocates [in order to] spread fear among other women’s rights activists [and] stop their activities,” says Rohgul Khairkhwah, an elected woman Senator for Nimroz province in southern Afghanistan and a recipient of the Ministry of Women’s Affairs ‘Bravest Woman in Afghanistan’ award (as quoted in the report). Senator Khairkhwah knows of what she speaks. On 4 August 2013, two days before the Muslim festival of Eid, the Taliban attacked her vehicle as she drove through Ghazni province on her way home. With her in the car were her husband and their three children, her brother and his three children. The Senator’s seven-year old daughter and brother were killed in the attack. Her other daughter, who was 11 at the time, was paralyzed as a result of her injuries. The Senator was shot nine times, sustaining wounds to her liver, lung and leg. She also lost a finger, and three others are now paralyzed. She spent the next two months in hospital recuperating from her injuries
(Burqas fail to shield many Afghan women from daily harassment, both in the street and at the workplace. Credit: Shelly Kittleson/IPS)
The report is the result of interviews with over 50 women defenders -- much like Khairkhwah -- and their family members across the country. Based on these, Amnesty International found a consistent pattern of authorities ignoring or refusing to take seriously threats against women. Few investigations were carried out, while prosecutions and convictions were even rarer. In many cases, women defenders who reported violence or attacks were put at further risk, facing stigmatization or threats simply for speaking out.
No woman in public life is safe – those facing threats and violence range from rights activists, politicians, lawyers, journalists, teachers. Even women in the police force are under threat, where sexual harassment and bullying is rife and almost always goes unpunished, the report said.
In eastern Laghman province, Dr Shah Bibi is the director of the Department of Women’s Affairs, and continues her work to strengthen women’s rights despite multiple death threats having forced her to move to a different province.
“Every day when I leave home I think that I will not return alive and my children are as scared as I am about a possible Taliban attack against me.”
Dr Bibi’s two predecessors – Najia Sediqi and Hanifa Safi – were killed within six months of each other in 2012, by gunmen in broad daylight and in a car bombing respectively. In a familiar story, relatives told Amnesty International how regular death threats had been met with no response by authorities, despite the women’s repeated pleas for protection. No one has been held responsible for their killings.
Despite the existence of a legal framework to protect women in Afghanistan – much of it thanks to tireless campaigning by women’s rights activists themselves – laws are often badly enforced and remain mere paper promises, the organisation states.
(The Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC) estimates a 22 percent increase in cases of violence against women. Marius Arnesen/CC-BY-SA-2.0. Credit: IPS)
The landmark Elimination of Violence against Women (EVAW) Law, passed in 2009, remains unevenly enforced and has only led to a limited number of convictions. Amnesty International’s investigation found that a lack of political will on the part of Afghan authorities means that government bodies and officials charged with protecting women are under-resourced and lack the support to carry out their work.
Added to this is a common acceptance of violence against women and girls as a “normal” part of life, and limits to their ability to participate freely in public life.
“The Afghan government is turning a blind eye to the very real threat women human rights defenders are facing. These brave people – many of them simply doing their jobs - are the bulwark against the oppression and violence that is part of daily life for millions of women across the country. The government must ensure they are protected, not ignored,” said Horia Mosadiq, Amnesty International’s Afghanistan Researcher.
While international governments have poured hundreds of millions of dollars into projects supporting women’s rights since 2001, the approach has not gone far enough. Projects have too often focused on short-term gains, and been implemented without consulting women’s activists themselves.
With the international troop withdrawal near completion, even these fragile gains are under threat.
The report follows a recent UN report that noted a 21 per cent increase in the number of women killed in Afghanistan in 2014 from 2013 with 298 women killed and 611 injured.